What is a Complex Correction in Elliott Wave?
In Elliott Wave theory, correcting complex patterns entails combining simple corrective waves (Zig-Zags, Flats, and Triangles) to build more elaborate structures. Complex corrections are designated as double threes or triple threes, depending on the number of component adjustments. Here are two types of complex corrections: Double Three and Triple Three.
In short
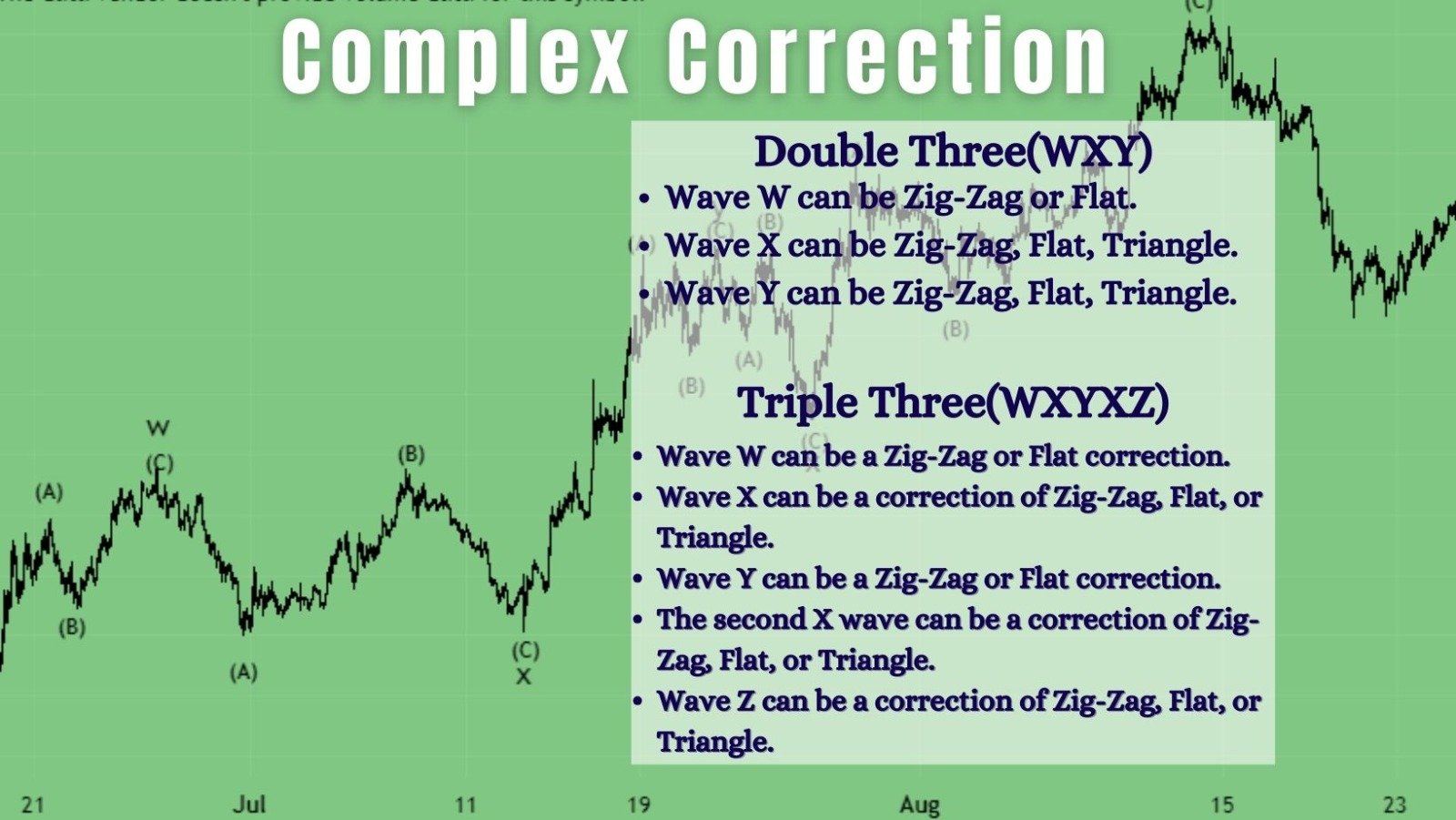
1. Double Three (WXY)
A Double Three correction in Elliott Wave theory involves a three-wave pattern with smaller sub-waves, repeating twice. This intricate structure adds layers of detail to market movement analysis, characterized by the repetitive nature of each wave’s subdivisions.
Characteristics of Double Three Correction
The Double Three correction is a pattern in Elliott Wave theory consisting of three waves, each representing a different type of correction. It is a pattern of repeated corrections within the overall structure, characterized by a series of corrections stacked on top of each other, similar to Zig-Zag or Flat corrections.

Key Points of Double Three Correction
- Comprises three wave moves: Zig-Zag or Flat.
- Each leg (w, x, y) represents a different correction.
- Imaged on market movement charts.
- Commonly seen in wave 4.
Patterns of Double Three Correction
- Wave w can be Zig-Zag or Flat.
- Wave x can be Zig-Zag, Flat, Triangle.
- Wave y can be Zig-Zag, Flat, Triangle.
Rules of Double Three Correction
1. Three Distinct Waves: A double three correction consists of three distinct waves named W, X, and Y.
2. Different Corrections in Each Leg: Each of the three legs (W, X, Y) has a different correction, such as Zig-Zag, Flat, or Triangle.
3. Structure Diversity: The corrective structures in each leg should be varied to ensure a diverse correction pattern.
4. Combination of Corrections: The pattern can be a combination of various corrective structures, allowing for flexibility in its formation.
5. Alternation Principle: The structures of W and Y should be alternated, such as W being a Zig-Zag, Y being a Flat or Triangle, and vice versa.
6. Subdivision within Legs: Elliott Wave theory’s fractal nature is evident in the smaller sub-waves found in each of its three legs (W, X, Y).
8. Pattern Repetition: The double three correction structure suggests a repetitive pattern of corrections, creating a layered effect on the price chart.
2. Triple Three (WXYXZ)
In Elliott Wave theory, the triple three correction emerges from a set of five waves, each of which contains smaller sub-waves. This complex corrective pattern consists of three sets of three waves.
Characteristics of Triple Three Correction
The Triple Three correction in Elliott Wave theory is a five-wave structure that moves counter to the larger trend. It shares similarities with the Ending Diagonal, but differs in its chart position. The Ending Diagonal develops in the direction of the larger trend, while the Triple Three correction moves against it. It’s not a diagonal pattern.

Key Points of Triple Three Correction
- Characterized by a five-wave structure moving counter to the larger trend.
- Similar to the Ending Diagonal, both share the same number of sub-waves.
- The difference lies in their position on the chart: the Diagonal develops in the direction of the larger trend, Triple Three moves against it.
- Often emerges in wave 4, especially when wave 2 was a straightforward correction.
- The similarity in sub-waves between Triple Three and Ending Diagonal emphasizes the complexity of both patterns.
Patterns of Triple Three Correction
- Wave W can be a Zig-Zag or Flat correction.
- Wave X can be a correction of Zig-Zag, Flat, or Triangle.
- Wave Y can be a Zig-Zag or Flat correction.
- The second X wave can be a correction of Zig-Zag, Flat, or Triangle.
- Wave Z can be a correction of Zig-Zag, Flat, or Triangle.
Rules of Triple Three Correction
1. Five-Wave Structure: A triple three correction is composed of a sequence of five waves, labeled W, X, Y, X, and Z.
2. Multiple Corrections: The corrective waves (W, X, Y) each have a unique correction type, such as Zig-Zag, Flat, or Triangle.
3. Variety in Corrections: The correcting structures mentioned inside the three legs should be diverse, avoiding uniformity.
4. Combination of Corrections: The triple three correction, similar to the double three, enables the incorporation of various corrective structures within its formation.
5. Alternation Principle: Alternation between the corrective structures of W and Y is essential for variety and complexity within the correction. For instance, if W is a Zig-Zag, Y might be a Flat or Triangle, and vice versa.
6. Subdivision within Legs: Each of the three main legs (W, X, and Y) is likely to have smaller sub-waves, reflecting the fractal nature of Elliott Wave theory.
7. Pattern Repetition: The price chart structure is enhanced by a repetitive pattern of triple three corrections.
Final thoughts
Elliott Wave theory’s complex corrections, such as double three and triple three corrections, are characterized by distinct characteristics, intricate patterns, and essential rules. These corrections combine structures like zigzags, flats, and triangles, showcasing the fractal essence of Elliott waves. Accurate identification requires understanding alternation principles, avoiding overlaps, and recognizing diversity within each leg. Understanding these patterns provides traders and analysts with a powerful tool to interpret and navigate market movements. This depth in Elliott Wave analysis empowers practitioners to make informed decisions in the ever-evolving financial markets.
FAQ
What is the 5 wave correction pattern?
The 5-wave correction pattern within the context of a triple three in Elliott Wave theory is usually recognized as a complicated correction. Unlike a simple Zigzag correction, the triple three involves three groups of three waves each, marked W, X, and Y. In the instance of the 5-wave pattern within a triple three, each of these waves (W, X, and Y) unfolds in a 5-3-5 structure, like a Zigzag correction. This elaborate pattern adds another layer of complexity to the overall correction, as each of the three main waves is made up of a series of five sub-waves. Understanding how these sub-waves interact is crucial for traders and analysts attempting to traverse the complexities of Elliott Wave patterns.